Password hygiene tips to follow include using unique passwords, enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and keeping your passwords safe in a password manager. Password hygiene encapsulates the
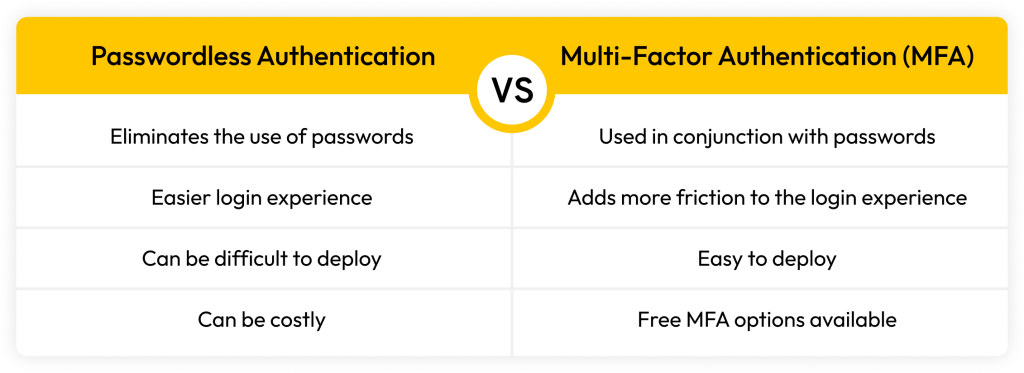
The main difference between passwordless authentication and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is that passwordless authentication completely removes the use of passwords, whereas MFA is used in conjunction with passwords. There are also differences in a user’s login experience when using passwordless authentication versus MFA, deploying each of them and their cost.
Continue reading to learn more about the differences between passwordless authentication and MFA.
What Is Passwordless Authentication?
Passwordless authentication is a method of verifying someone’s identity in order to log in to an account or application without having to enter a password. Passwordless authentication enables secure logins by identifying that an account belongs to a user by using other factors such as biometrics. Biometrics include anything related to someone’s physical or behavioral characteristics such as fingerprints, facial recognition and voice patterns, to name a few.
Passwordless authentication examples
- Biometrics
- Magic links
- Passkeys
What Is Multi-Factor Authentication?
Multi-factor authentication is a security measure that adds an additional layer of protection to accounts. Rather than only having to enter a username and password, with MFA enabled, users must take an additional step to authenticate their identity with another method of authentication. Other methods of authentication can include biometric authentication or providing a Time-based One-Time Password (TOTP) code from an authenticator app.
Multi-factor authentication examples
- Username and password plus biometrics
- Username and password plus a hardware security key
- Username and password plus a TOTP code from an authenticator app
Key Differences Between Passwordless Authentication and MFA
Here are some of the key differences between passwordless authentication and MFA.
Use of passwords
The biggest difference between passwordless authentication and MFA is that passwordless authentication eliminates the use of passwords. This differs from MFA which is used in conjunction with a username and password. When MFA is enabled on an account, users still have to enter their username and password. If the username and password are associated with an account, the user will then be prompted to authenticate their identity with another method of authentication.
Login experience
When it comes to the login experience, passwordless authentication has the most seamless login experience because there’s no need for users to enter a password. When using MFA on the other hand, some users may find that their login experience takes more time and adds more friction. This is especially true for users who choose to use an authenticator app as an MFA method. Authenticator apps are typically downloaded on a user’s phone so the user will always have to have their phone with them when authenticating their identity.
Difficulty to employ and cost
For organizations, implementing passwordless authentication for employees isn’t as easy as it seems because it requires that the accounts, applications and software being used support passwordless authentication. Investing in software that does support passwordless authentication can also be costly for organizations. MFA isn’t as difficult to deploy because it can be as simple as having employees download an authenticator app and using it to authenticate themselves when signing in to an account. Most authenticator apps are free so they don’t require that organizations increase their spending.
Is Passwordless Authentication Safer To Use Than MFA?
While both passwordless authentication and MFA increase your account’s security, passwordless authentication is considered to be more secure because it removes the use of passwords altogether. Any account that uses passwords is susceptible to being compromised as a result of password-related attacks and social engineering. Because passwordless authentication removes the use of passwords, password-related attacks are no longer relevant. In terms of social engineering, cybercriminals can’t trick users into handing over their biometrics like they can with passwords.
Let’s take passkeys as an example. Passkeys are a new passwordless authentication technology that allow users to sign in to their online accounts without having to enter a password. Instead, users authenticate the same way they sign in to their devices or password manager applications. Most users will choose to sign in using biometrics for convenience.
Passkeys are tied to the device or password manager they’re created on, so that device or password manager is always needed to sign in with it. Passkeys are safer to use than a password combined with MFA, because they’re phishing-resistant, so they can’t be as easily compromised like passwords.
Use Passwordless Authentication and MFA
Not all websites and applications support the use of passwordless authentication, so users will still have to use strong passwords and MFA for some accounts, systems and applications. Enabling MFA still greatly increases the security of an account by adding an additional layer of authentication, so it should be enabled whenever it’s an option.
For organizations who want to start using passwordless authentication, strong passwords and MFA should be used while you make the transition. Keeper® can help organizations transition to a fully passwordless environment through integration with Single-Sign On (SSO) or passwordless providers, and by providing organizations with a way to securely store, manage and autofill both passwords and passkeys.
Curious to learn more about how Keeper can help organizations achieve a fully passwordless environment? Request a demo today.
 Password
Password