No, it’s not safe to password-protect PDF files because your files are not guaranteed to be protected from cybercriminals intercepting and gaining unauthorized access to your
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) has become a cybersecurity necessity for protecting online accounts. It ensures that only authorized users can access an account. However, when picking an MFA method, some options are more secure than others. An authenticator app is safer than SMS authentication because it generates 2FA codes locally, which prevents cybercriminals from intercepting the codes as they can with SMS.
Continue reading to learn more about authenticator apps, SMS authentication, why authenticator apps are more secure than SMS authentication and how to set up an authenticator app.
What Is an Authenticator App?
An authenticator app is an application used as an additional verification method for MFA. It generates a code locally on your device that you use alongside your login credentials to access your online accounts. These authenticator app codes are known as Time-based One Time Passwords (TOTP). TOTPs are unique six to eight-digit codes that last for 30 to 60 seconds. After every 30 to 60 seconds, the authenticator app generates a new, unique TOTP code based on a secret algorithm.
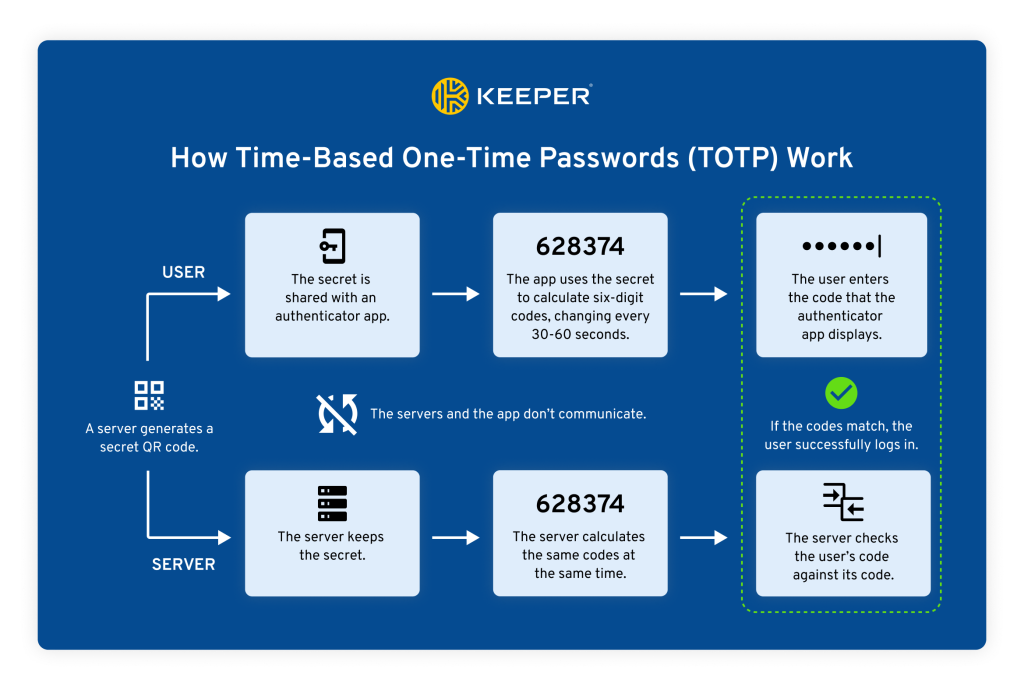
Authenticator apps work based on the TOTP verification model. When a user is setting up MFA for their account, they can choose TOTP for their MFA method. This will trigger the account server to create a QR code for the authenticator app to scan or a secret key that can be inputted manually. The QR code and key contain a secret algorithm that generates TOTP codes in real time. After the user has finished setting up their authenticator app, both the authenticator app and the account server will independently generate the same code simultaneously.
When the user tries to log in to their account, they will enter their login credentials along with the TOTP code from their authenticator app. The account server will then check the user’s TOTP code to see if it matches the same code that the account server generated. If the codes match, the user is granted access to the account. If the codes don’t match, the user is denied access to the account.
What Is SMS Authentication?
SMS authentication is a type of authentication method that verifies a user’s identity with a code that is sent to them via text message. These codes are One-Time Passwords (OTP) which are generated for one-time use. OTPs can last for 30 seconds to an hour, and users must request a new OTP after the time limit if needed.
When creating an account, users are often asked to provide their phone number, which the account server uses to send them an OTP code. To access their account, users must provide their login credentials along with the OTP code they receive over text. Email authentication is the same as SMS authentication, but it uses an email address instead of a phone number to send the OTP codes.

Why You Should Use an Authenticator App Over SMS
You should use an authenticator app over SMS authentication because it is more secure and less likely to be intercepted by cybercriminals. Authenticator apps generate 2FA codes locally on a device, rather than sending them unencrypted over text message. The 2FA codes in authenticator apps also change every 30 to 60 seconds, which makes them difficult for cybercriminals to steal.
SMS authentication sends 2FA codes unencrypted over text message. SMS 2FA codes can easily be compromised by man-in-the-middle attacks and SIM swapping.
- Man-in-the-middle attack: A type of cyber attack in which cybercriminals intercept transmitted data over an unencrypted WiFi network. If a user is connected to a fabricated or public WiFi network, cybercriminals can eavesdrop, steal or modify the user’s internet traffic, including 2FA codes.
- SIM swapping: When cybercriminals impersonate a victim to convince a mobile carrier to activate a new SIM card with the victim’s phone number. Cybercriminals will then receive the victim’s text messages and phone calls, which they can use to steal SMS 2FA codes.
Since authenticator apps generate 2FA codes locally, the codes cannot be intercepted by cybercriminals. The only ways to steal 2FA codes from an authenticator app is by compromising the device with malware, through social engineering or by physically stealing the device; however, these methods could be used to steal SMS codes as well. Another way to potentially steal 2FA codes from authenticator apps is by stealing the QR code which is uncommon and very difficult. Users can easily protect an authenticator app’s 2FA codes by protecting their device with a PIN, avoiding malware and social engineering, and keeping the QR and 2FA codes hidden.
How To Set Up an Authenticator App
Setting up MFA with an authenticator app is easy. Here are the steps to setting up an authenticator app:
- Choose an authenticator app: Not all authenticator apps are the same. You need to choose an authenticator app that fits your needs. We recommend using a password manager since some password managers can generate and store 2FA codes in a digital password vault.
- Download the authenticator app on your device: If you are using a standalone authenticator app, you need to download the app on your device. You should download the authenticator app on your phone to always have access to it.
- Enable MFA on your account: After downloading the authenticator app, you need to log in to your account and enable MFA. Pick the setting that allows you to use an authenticator app as your MFA method. Your account will then show you the QR code and secret key with the algorithm that generates TOTPs.
- Scan the QR code or enter the secret key with the authenticator app: Next, you need to scan the QR code with the authenticator app, or manually enter the secret key, so the authenticator app can generate the same TOTP codes as the account server.
- Ready to go: You have now set up your authenticator app as your MFA method for your account. The next time you try to log in to your account, you will use the TOTP from your authenticator app to gain access. You will need to repeat steps 3 and 4 whenever you try to set up MFA for your other accounts.
How Password Managers Protect Your Accounts With Integrated 2FA
Although using SMS authentication is better than not having MFA enabled at all, you should use an authenticator app over SMS authentication because it is more secure. Authenticator apps are convenient, secure and free, making them a better option for MFA.
You may be able to use a password manager as your MFA method. Some password managers have integrated authenticator apps that will generate and store 2FA codes for your accounts. Using a password manager makes it easier to log in to your accounts since you have access to your login credentials and 2FA codes from any device. Some password managers offer an autofill feature that fills in your login credentials and 2FA codes when you try to log in.
Keeper Password Manager has integrated authenticator app features, allowing you to generate 2FA codes whenever you try to log in to your accounts. It also comes with the KeeperFill feature which automatically fills your login credentials and 2FA codes whenever you try to log in to your accounts. Sign up for a free trial to protect your accounts with strong MFA.
 Password
Password 
