Privileged credential theft
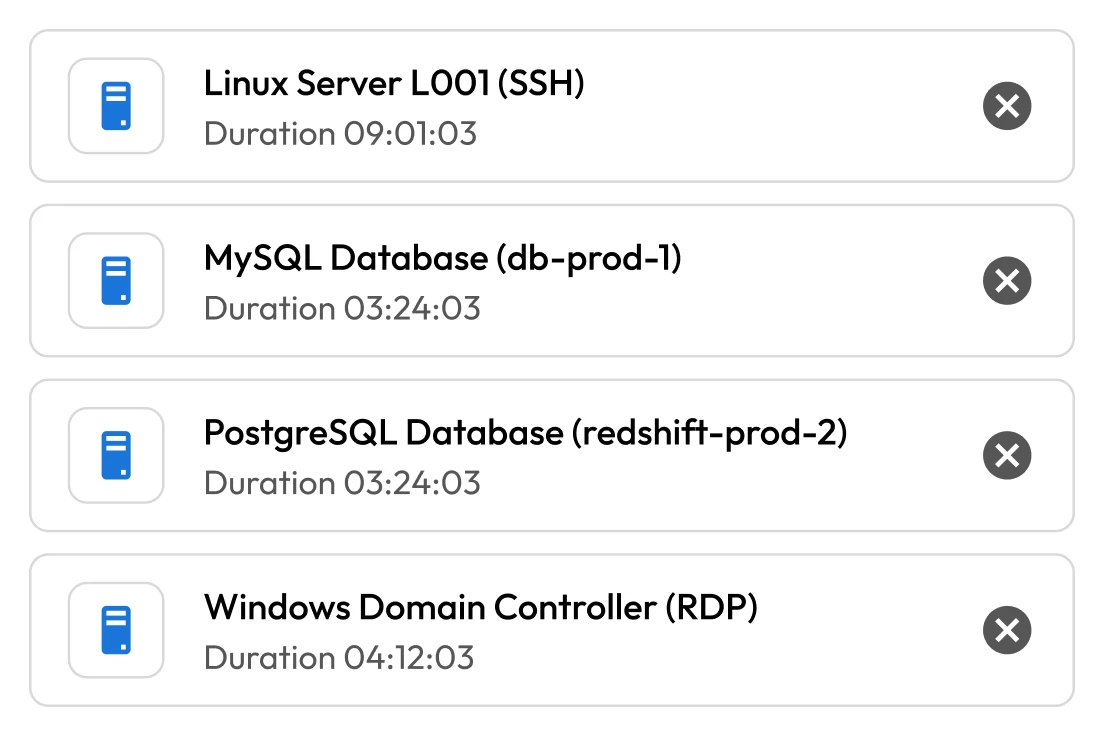
Cybercriminals often target internal admin and DevOps credentials through phishing or malware. These privileged accounts provide direct access to critical systems, and once compromised, can allow cybercriminals to move freely within the environment, often without immediate detection.
Insider threats
Employees, contractors and partners with privileged access can pose serious security risks. Whether through carelessness or intentional misuse, these insiders can compromise systems, expose sensitive data and disrupt operations, especially in environments where privileged access is not tightly controlled or monitored.
Lack of least-privilege controls
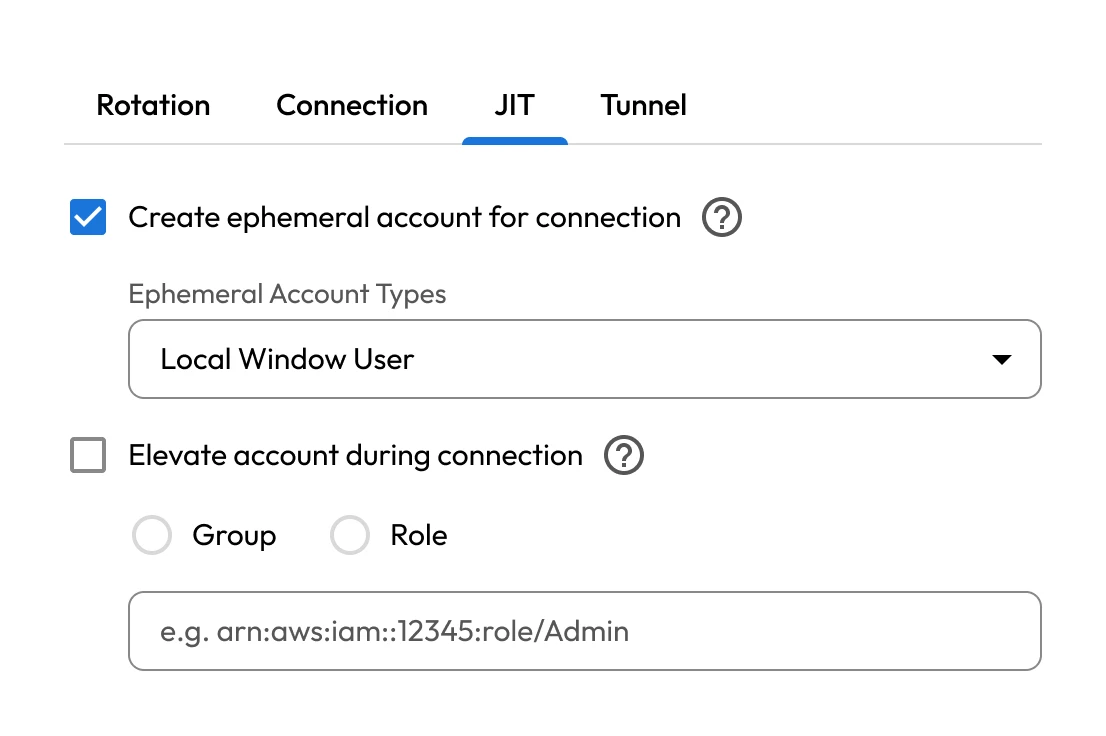
Over-privileged accounts and misconfigured roles are common issues in SaaS environments. Employees are often granted broader access than necessary, increasing the potential impact if an account is misused. Without strict enforcement of least-privilege principles, users can gain unnecessary access to sensitive systems.
Poor secrets management
Many SaaS organizations struggle to manage credentials securely across their DevOps environments. Secrets are frequently embedded in scripts, configuration files or code repositories like GitHub, where they can be exposed during development or deployment. These practices create unnecessary risk and leave critical systems vulnerable to misuse or compromise.
Insufficient monitoring of privileged activities
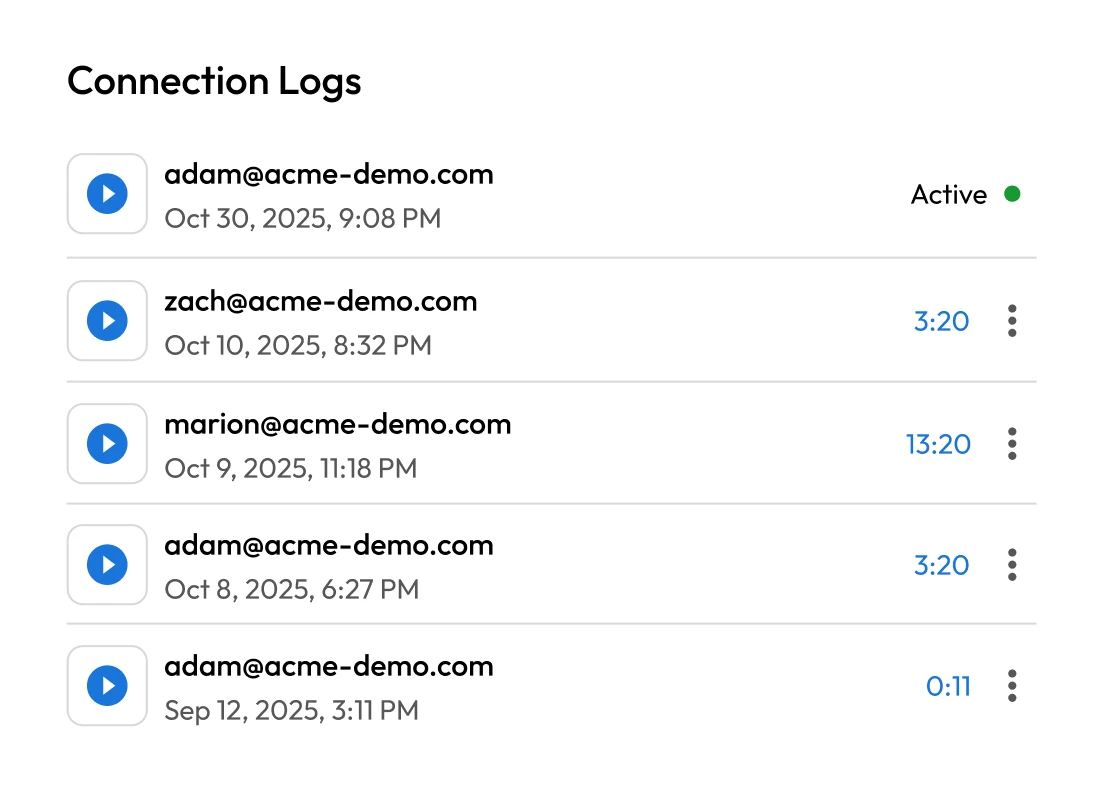
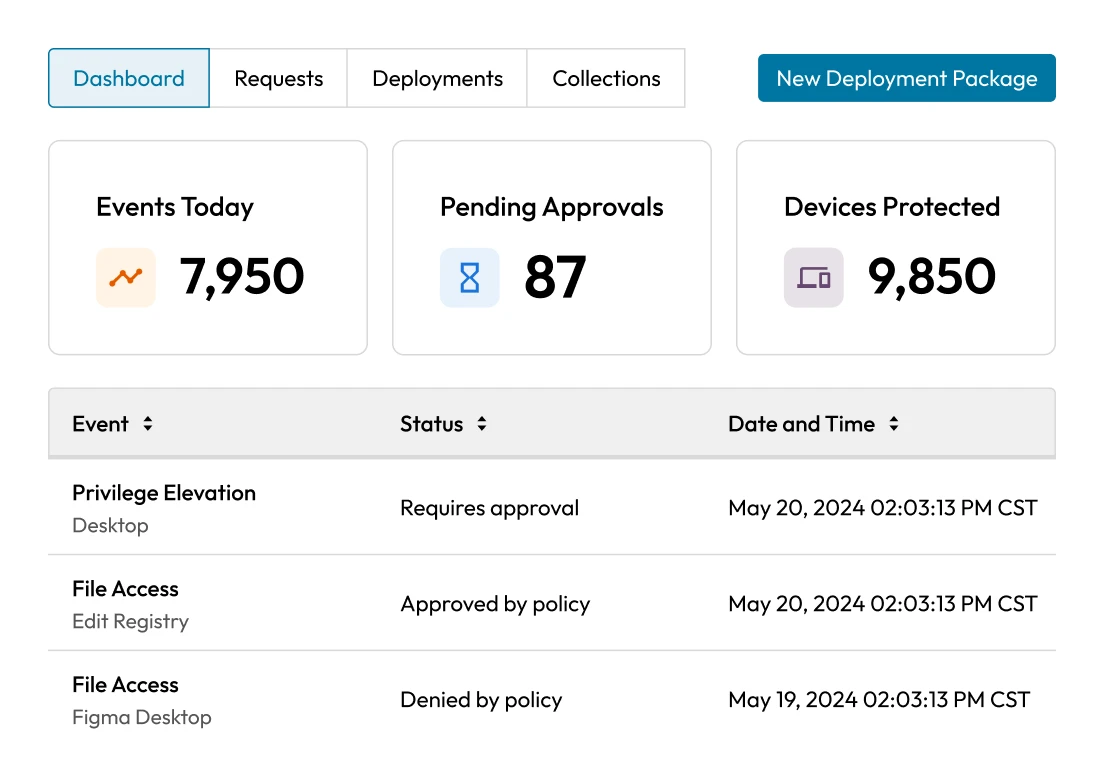
Without real-time oversight, privileged account misuse can escalate quickly and remain unnoticed until serious damage occurs. Inadequate auditing, lack of behavior analytics or missing alerts tied to privileged activity can make it difficult to detect anomalies or unauthorized actions. These visibility gaps leave room for cybercriminals or insiders to exploit elevated access.
Third-party access risks
SaaS companies often rely on external developers, consultants and integration partners who require temporary or limited access to internal systems. Without granular access controls and session monitoring, third-party access creates a major security gap. These external users can retain more access than needed or longer than intended, increasing the risk of misuse or compromise.